Setting Up a WalletIntroduction
Setting up an Ethereum wallet is the first step towards engaging with the Ethereum blockchain and its ecosystem of decentralized applications (DApps) and digital assets. In this chapter, we will explore the process of setting up an Ethereum wallet, the different types of wallets available, and the importance of security in protecting your funds.
1. Understanding Ethereum Wallets
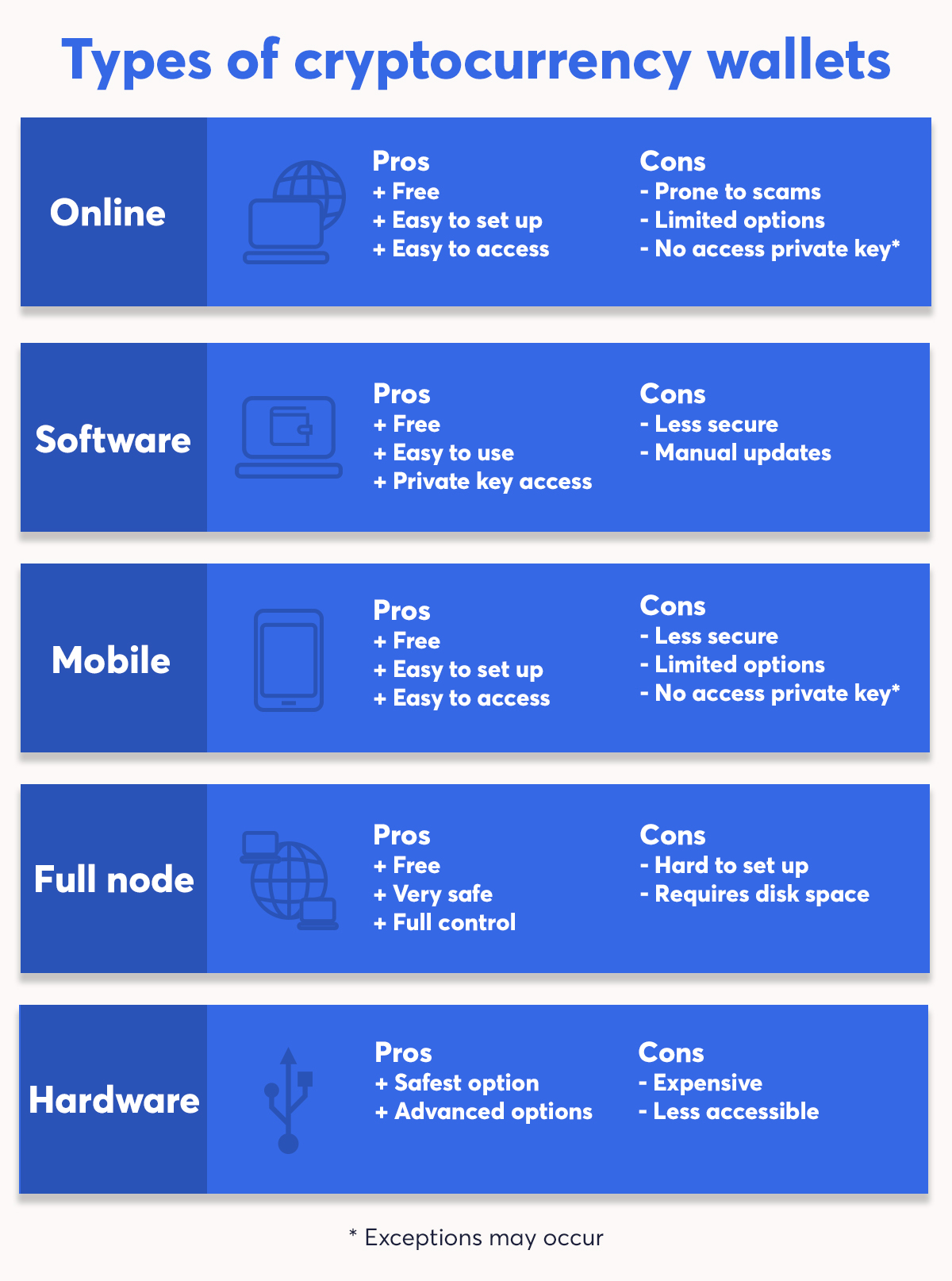
Ethereum wallets are software applications that allow users to securely store, send, and receive Ether (ETH) and other Ethereum-based tokens. There are several types of wallets, each offering different levels of security, accessibility, and functionality:
-
Software Wallets: These wallets are applications that run on desktop computers, mobile devices, or web browsers. They provide convenient access to your funds but may be susceptible to hacking or malware if not properly secured.
-
Hardware Wallets: Hardware wallets are physical devices that store your private keys offline, providing an extra layer of security against online threats. They are ideal for long-term storage of large amounts of Ether and are considered one of the most secure wallet options.
-
Paper Wallets: Paper wallets involve printing out your private key and public address on a physical piece of paper. While paper wallets offer excellent security as they are not susceptible to hacking, they require careful handling to prevent loss or damage.
anycoindirect
2. Steps to Setting Up a Wallet
The process of setting up an Ethereum wallet typically involves the following steps:
-
Choose a Wallet: Select a wallet that best fits your needs and preferences. Consider factors such as security, convenience, and platform compatibility when making your decision.
-
Download or Access the Wallet: Depending on the type of wallet chosen, download the software application, access the web-based platform, or connect the hardware device to your computer or mobile device.
-
Generate a New Wallet: Follow the instructions provided by the wallet provider to generate a new Ethereum wallet. This typically involves creating a strong password or PIN and securely storing your recovery phrase or seed phrase.
-
Backup Your Wallet: Backup your wallet's recovery phrase and store it in a safe and secure location. This recovery phrase is crucial for recovering access to your wallet in case your device is lost, stolen, or damaged.
-
Receive and Send Ether: Once your wallet is set up and secured, you can receive Ether by sharing your public address with others or sending Ether by entering the recipient's address and the amount you wish to send.
Conclusion
Setting up an Ethereum wallet is a crucial step towards engaging with the Ethereum blockchain and participating in its decentralized ecosystem. By following the steps outlined in this chapter and choosing a wallet that meets your security and usability requirements, you can safely store your Ether and interact with decentralized applications and digital assets on the Ethereum network.